Difference between revisions of "Vector displacement map"
From polycount
(→Vector Displacement Map) |
EricChadwick (Talk | contribs) (restoring images) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Vector Displacement Map = | = Vector Displacement Map = | ||
| − | + | [[image:vectordisp_vs_disp.jpg|frame|left|Displacement vs. vector displacement, from the [http://download.autodesk.com/us/systemdocs/help/2011/mudbox/files/WS73099cc142f487552b5ac6c412649166e6e-6762.htm Mudbox 2011 Help file]. (Note: the vector map is a HDR image, so the full range can't be displayed properly). Image by [http://www.autodesk.com/ Autodesk].]]<br clear="all"/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Traditional grayscale [[Displacement map|displacement mapping]] encodes the difference between the high-resolution model and the low-resolution model, using the low-res model's UV coordinates. Vector displacement uses a similar process, except it also uses the high-res model's UV coordinates, creating a correspondence between the two UVs. | Traditional grayscale [[Displacement map|displacement mapping]] encodes the difference between the high-resolution model and the low-resolution model, using the low-res model's UV coordinates. Vector displacement uses a similar process, except it also uses the high-res model's UV coordinates, creating a correspondence between the two UVs. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 6: | ||
This correspondence allows the map to encode not only how far away one vertex is from the nearest vertex on the other mesh, but also to move the vertex across all three axes in space. This allows the map to encode complex undercuts, for example under a mushroom cap or behind an ear. | This correspondence allows the map to encode not only how far away one vertex is from the nearest vertex on the other mesh, but also to move the vertex across all three axes in space. This allows the map to encode complex undercuts, for example under a mushroom cap or behind an ear. | ||
| − | + | [[image:vectordisp_ear_youtube.jpg|frame|left|Vector displacement of an ear in Mudbox 2011 ([http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZPezIU0c4zc Youtube video]). Image by [http://www.dashdotslash.net/ Wayne Robson].]]<br clear="all"/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
== Related Pages == | == Related Pages == | ||
Revision as of 17:22, 17 May 2015
Vector Displacement Map
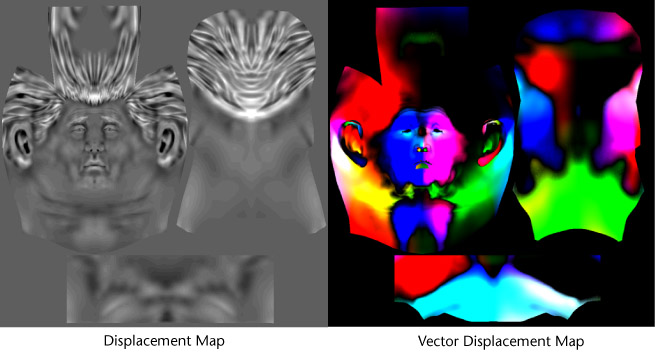
Displacement vs. vector displacement, from the Mudbox 2011 Help file. (Note: the vector map is a HDR image, so the full range can't be displayed properly). Image by Autodesk.
Traditional grayscale displacement mapping encodes the difference between the high-resolution model and the low-resolution model, using the low-res model's UV coordinates. Vector displacement uses a similar process, except it also uses the high-res model's UV coordinates, creating a correspondence between the two UVs.
This correspondence allows the map to encode not only how far away one vertex is from the nearest vertex on the other mesh, but also to move the vertex across all three axes in space. This allows the map to encode complex undercuts, for example under a mushroom cap or behind an ear.
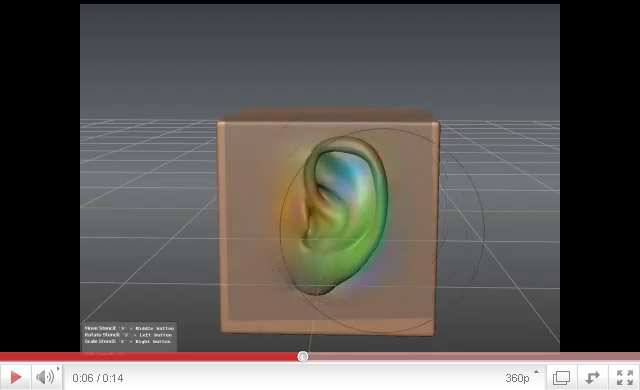
Vector displacement of an ear in Mudbox 2011 (Youtube video). Image by Wayne Robson.
Related Pages
- Curvature map
- DuDv map
- Flow map
- Normal map
- Radiosity normal map
- Vector displacement map